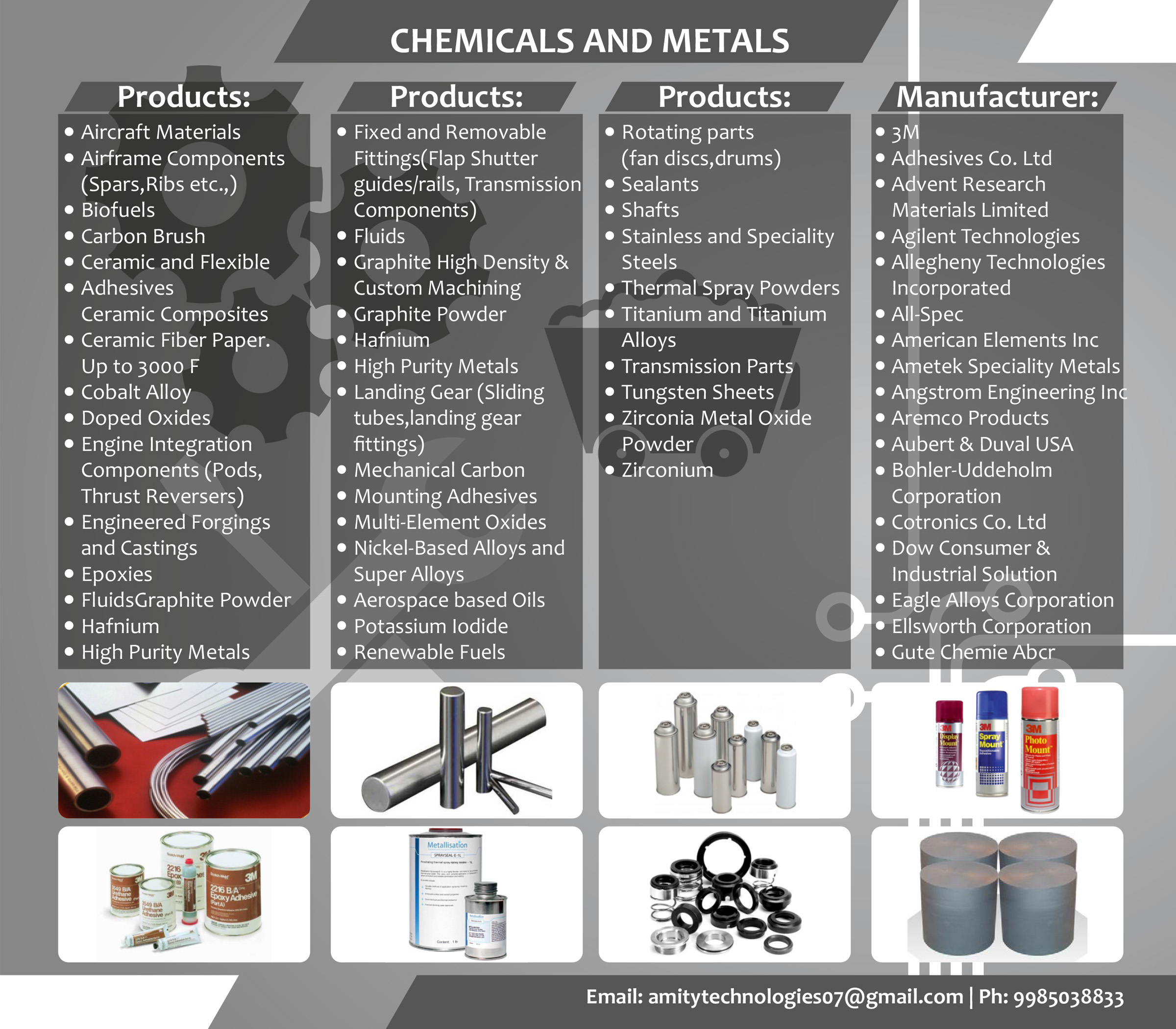
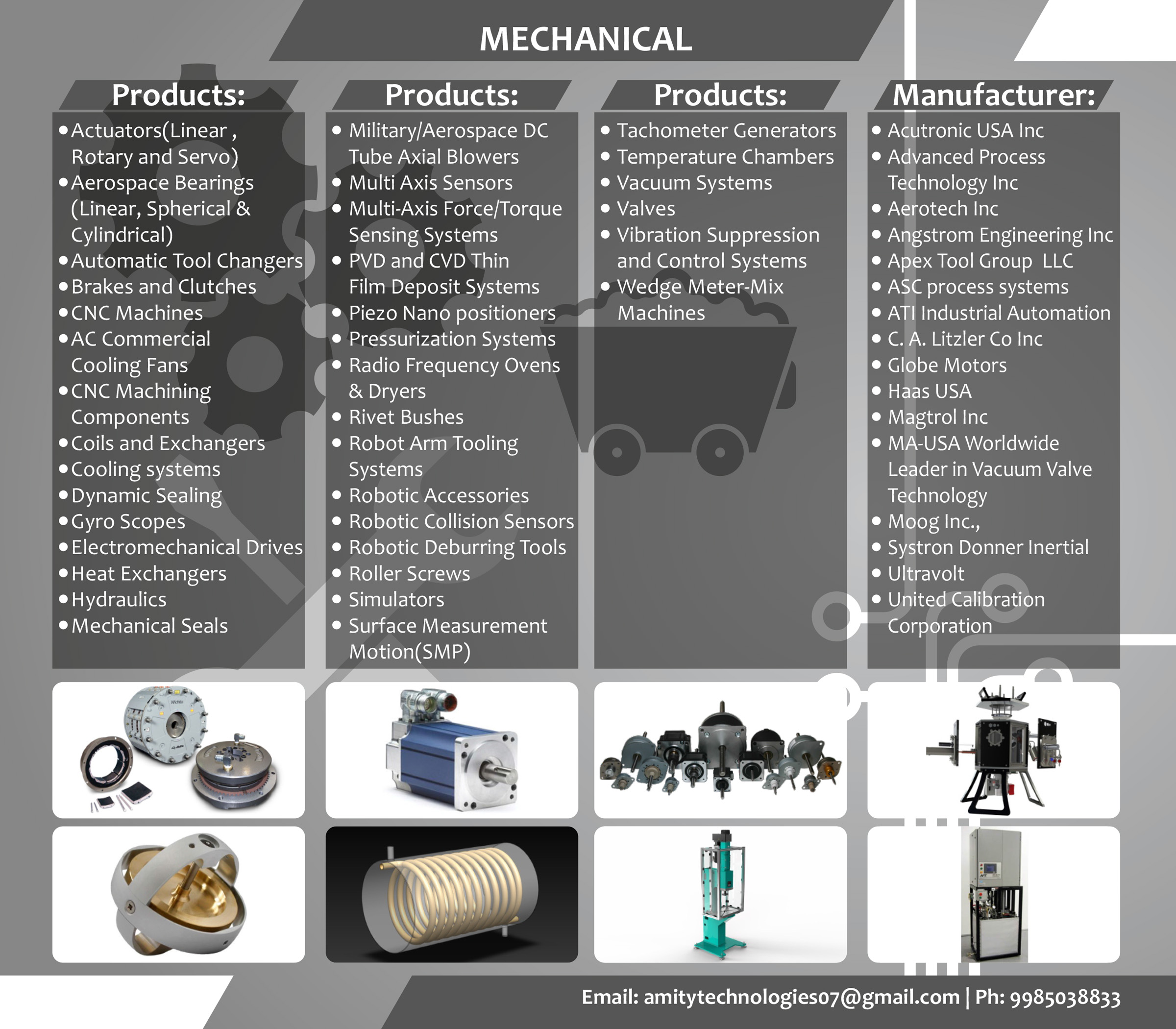
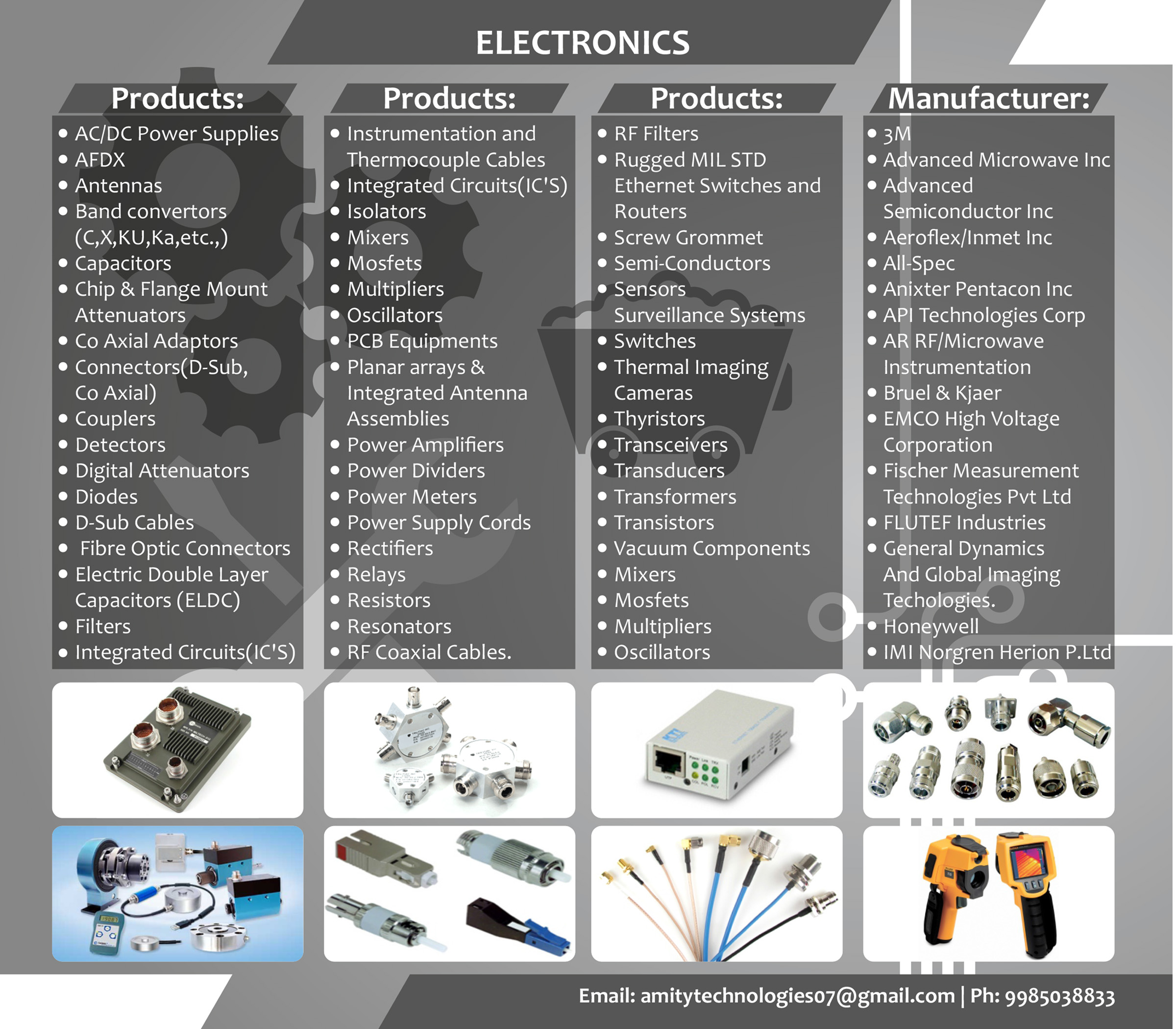
In modern defence operations, the ability to communicate securely and reliably can mean the difference between mission success and failure. As threats evolve—from sophisticated cyberattacks to advanced electronic warfare—secure communication systems have become a cornerstone of military readiness. This article explores the latest trends and technologies shaping secure communications for defence forces worldwide.
Why Secure Communications Matter in Defence
Defence communications must handle high volumes of sensitive data, including mission plans, troop movements, surveillance feeds, and intelligence reports. These systems face three major challenges:
- Confidentiality – Preventing interception and eavesdropping.
- Integrity – Ensuring that transmitted data is not altered or tampered with.
- Availability – Guaranteeing uninterrupted communication, even in hostile or remote environments.
In battlefield situations, secure communication is not just about protecting data—it’s about protecting lives.
Key Trends in Defence Communication Systems
1. Shift Towards Software-Defined Radios (SDRs)
Software-defined radios are replacing traditional hardware-based communication systems. SDRs allow military operators to reconfigure frequencies, encryption standards, and communication protocols on the fly—offering flexibility to adapt to evolving threats.
Benefits:
- Interoperability across multiple platforms
- Remote updates without hardware changes
- Enhanced resilience against jamming
2. Adoption of Quantum Communication
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is emerging as a game-changer for ultra-secure communications. Using quantum mechanics principles, QKD ensures that any interception attempt is immediately detectable.
Applications:
- Secure satellite-to-ground links
- High-security data centres
- Strategic command communications
3. Integration of AI for Signal Protection
Artificial Intelligence is being deployed to detect jamming, identify unusual signal patterns, and optimize frequency usage in real time. AI-driven spectrum management improves the survivability of communication channels during electronic warfare.
4. Satellite-Based Secure Networks
Next-generation military satellites offer global coverage, encrypted channels, and anti-jamming capabilities. Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations are reducing latency, enabling near real-time secure video and data exchange.
5. End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
Modern defence communication systems employ advanced encryption algorithms like AES-256 and post-quantum cryptography to protect messages from interception, even by future quantum computers.
Technologies Powering the Future of Secure Defence Communications
| Technology | Function | Defence Application |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh Networking | Creates self-healing networks | Troop-to-troop and unit communications in remote terrain |
| Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) | Rapidly changes frequencies to avoid interception | Air-to-ground and ship-to-ship communication |
| Post-Quantum Cryptography | Resists quantum attacks | Long-term secure storage and transmission of classified data |
| Adaptive Beamforming Antennas | Directs signals precisely towards intended receivers | Reduces detection risk and improves signal quality |
| Zero Trust Architecture | Continuous authentication and monitoring | Secure network access for military cloud systems |
Challenges Ahead
While these innovations are promising, defence communications still face critical hurdles:
- Cyber Threats: State-sponsored hackers and cyber-espionage.
- Spectrum Congestion: Increased competition for bandwidth in both civilian and military domains.
- Interoperability: Coordinating communication systems across allied forces with different standards.
Conclusion
Secure communication systems are the nervous system of modern defence forces. With advancements in SDRs, quantum encryption, AI-assisted signal protection, and satellite networks, militaries are better equipped to ensure that their communications remain secure, reliable, and adaptive to the challenges of tomorrow. However, continued investment, interoperability standards, and robust cyber defences are essential to stay ahead of adversaries in an increasingly contested information environment.